Advanced Guide to tmux: Enhancing Terminal Productivity

What is tmux?
tmux stands for terminal multiplexer. It enables users to access multiple separate terminal sessions inside a single terminal window or remote terminal session. It's especially useful for maintaining command-line programs running without being connected to them.
Key Features of tmux
- Session Management: Safely detach and reattach to terminal sessions.
- Windows and Panes: Organize your workspace by creating multiple windows and dividing them into panes.
- Customization: Modify your environment through a tmux configuration file,
.tmux.conf. - Clipboard Support: Seamlessly copy and paste between sessions and panes.
Installation
Installing tmux on Linux
For Debian-based distributions (like Ubuntu), you can use apt:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install tmuxFor Red Hat-based distributions (like Fedora or CentOS), you can use yum or dnf:
sudo dnf install tmuxor
sudo yum install tmuxInstalling tmux on macOS
You can install tmux using Homebrew, a popular package manager for macOS:
brew install tmuxInstalling tmux on Windows
Installing tmux on Windows is a bit more involved as it's not natively supported. However, you can use tmux within the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). First, ensure that WSL is installed, and then install tmux in your Linux distribution following the Linux instructions above.
Once tmux is installed, you can launch it by typing tmux into your terminal. If you're new to tmux, you may want to spend some time learning the basic commands and configurations to make the most out of your tmux experience.
Deep Dive into Practical Use Cases
1. Persistent Sessions Across Connections
This is particularly useful for maintaining development environments or long-running jobs on remote servers, ensuring they continue to operate even if your connection is interrupted.
Detailed Example:
Start a new tmux session named 'dev'
tmux new -s dev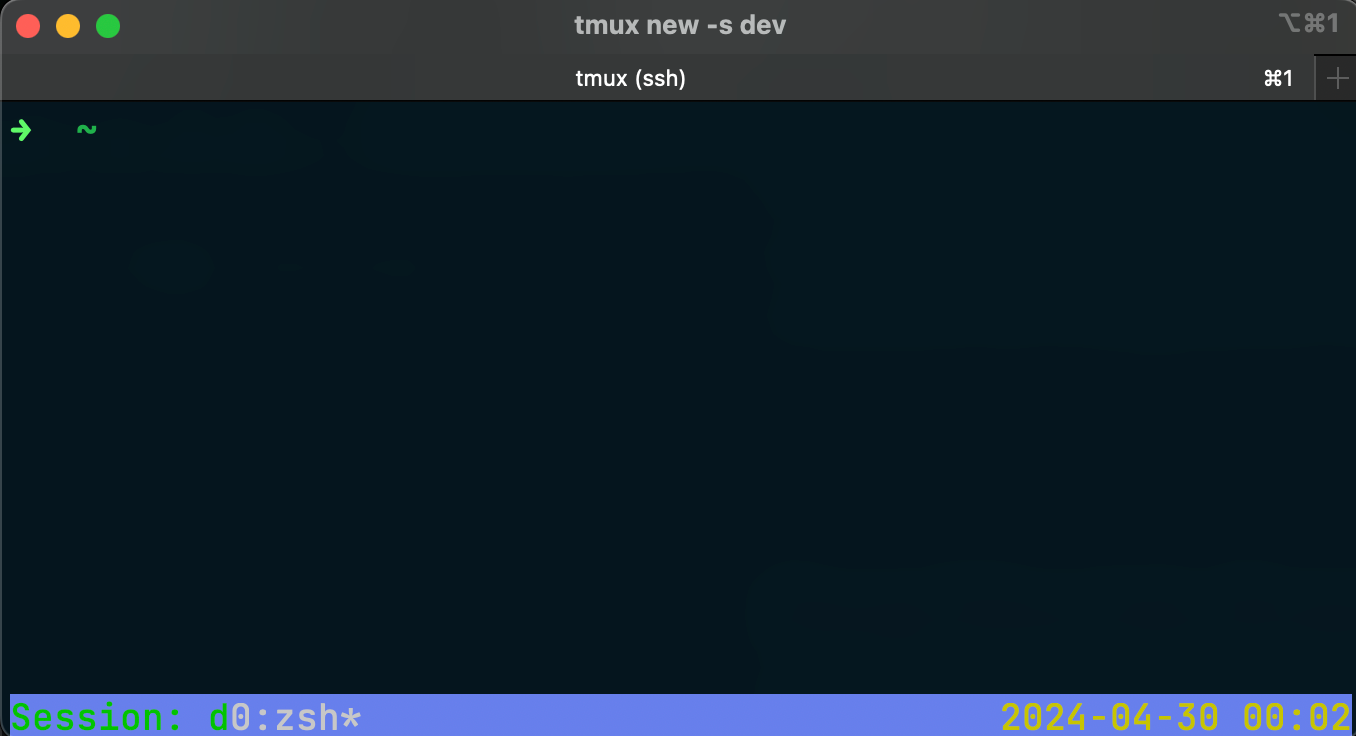
Detach from the session
Ctrl-b d # 'Ctrl-b' is the default command prefix, followed by 'd' to detach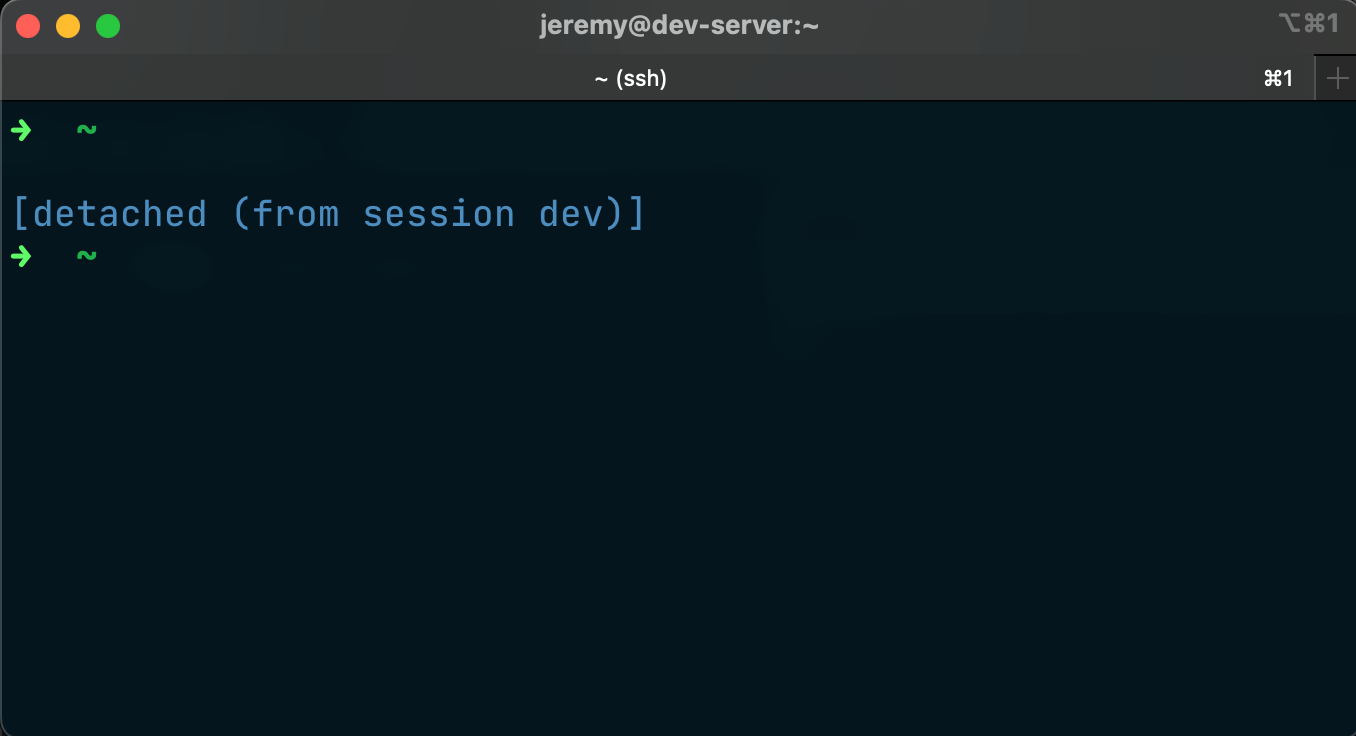
Resume your session from anywhere
tmux attach -t dev2. Managing Multiple Projects Simultaneously
tmux excels in handling several projects by organizing them into different windows within the same session, each dedicated to a specific task or project.
Step-by-Step Example:
Create a new window
Ctrl-b cNavigate between windows using shortcuts
Ctrl-b p # Move to the previous window
Ctrl-b n # Move to the next window3. Complex Workspace Setups
Easily split your windows into multiple panes, which is ideal for monitoring servers, editing code, and running scripts side by side.
Advanced Pane Management:
Split the current window into two horizontal panes
Ctrl-b " # Use double quote to split horizontally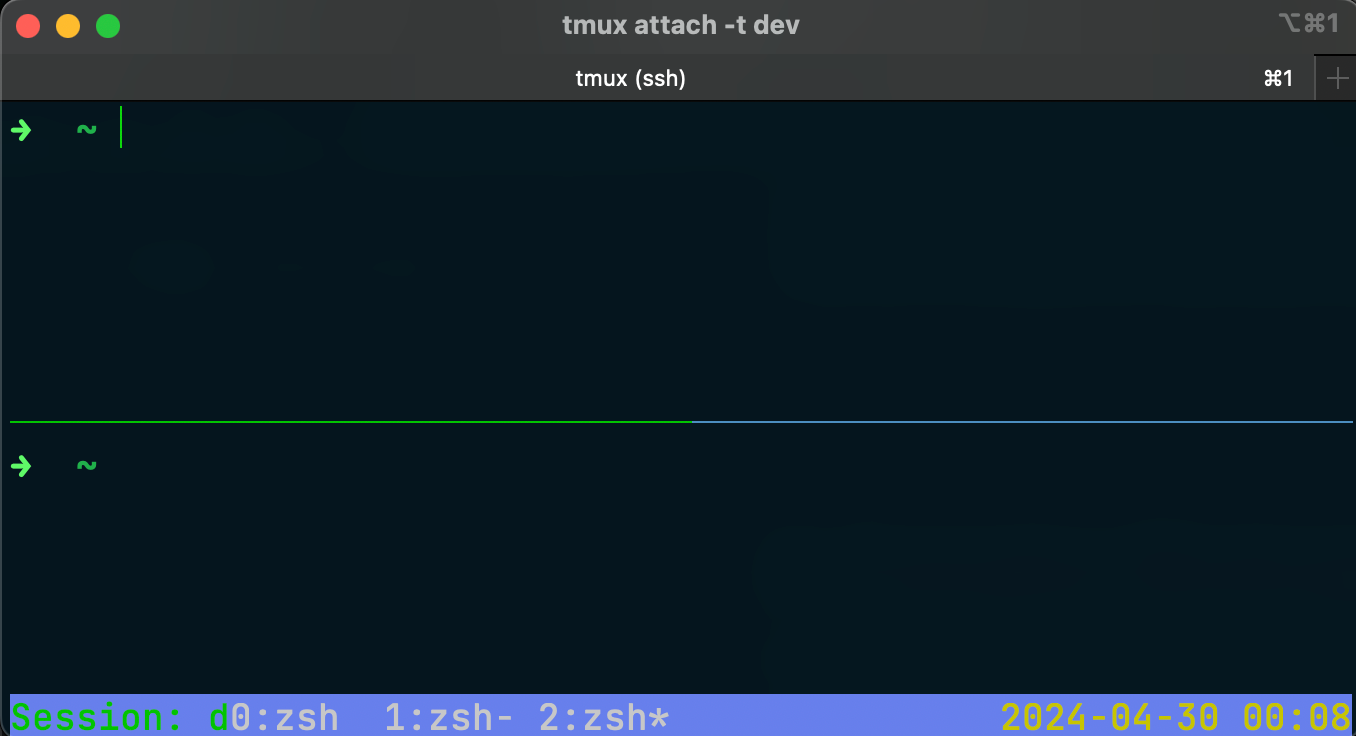
Create a vertical split in one of the existing panes
Ctrl-b % # Use percent sign for vertical split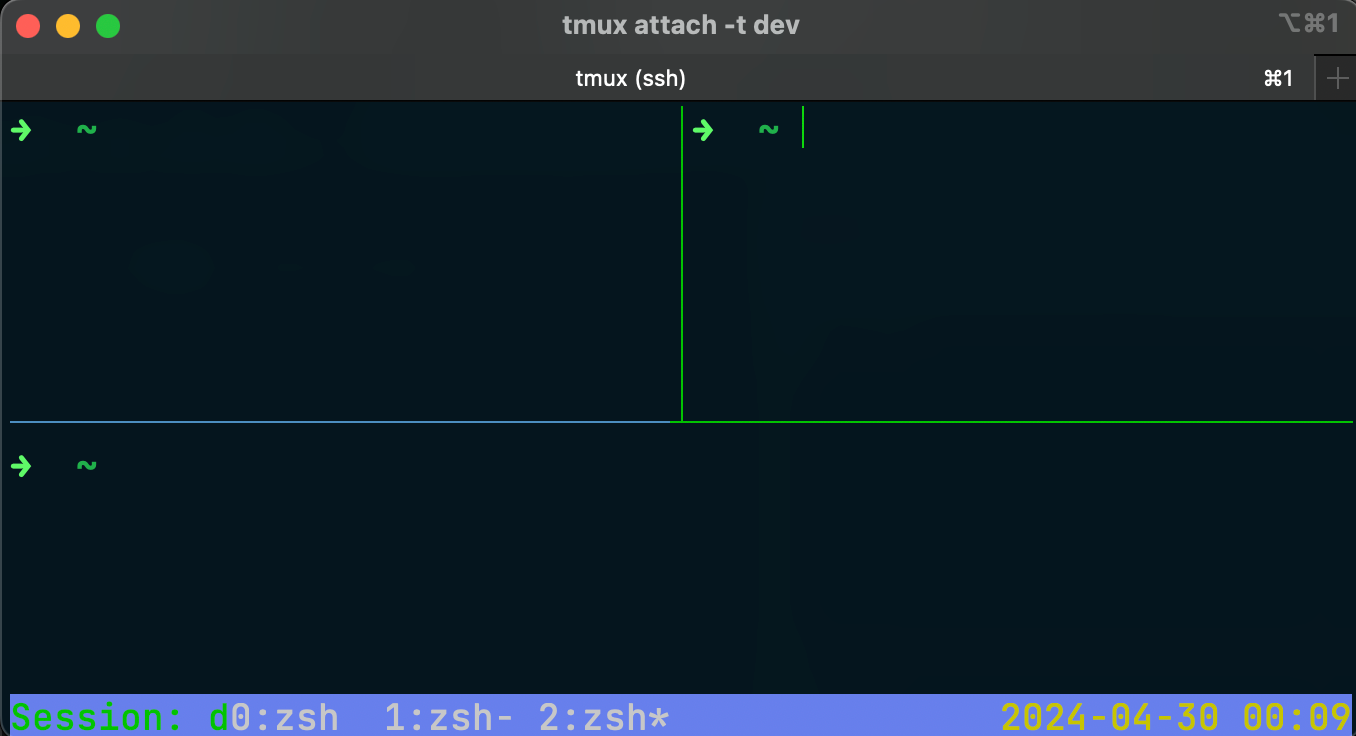
Navigate between panes
Ctrl-b arrow keys # Use arrow keys to move focus between panes4. Session Scripting and Automation
Automate the creation of sessions with pre-defined windows and panes, tailored to your workflow needs.
Automation Script Example:
Start a new session, open vim in the first pane
tmux new-session -d -s 'Code' -n 'Editor' 'vim'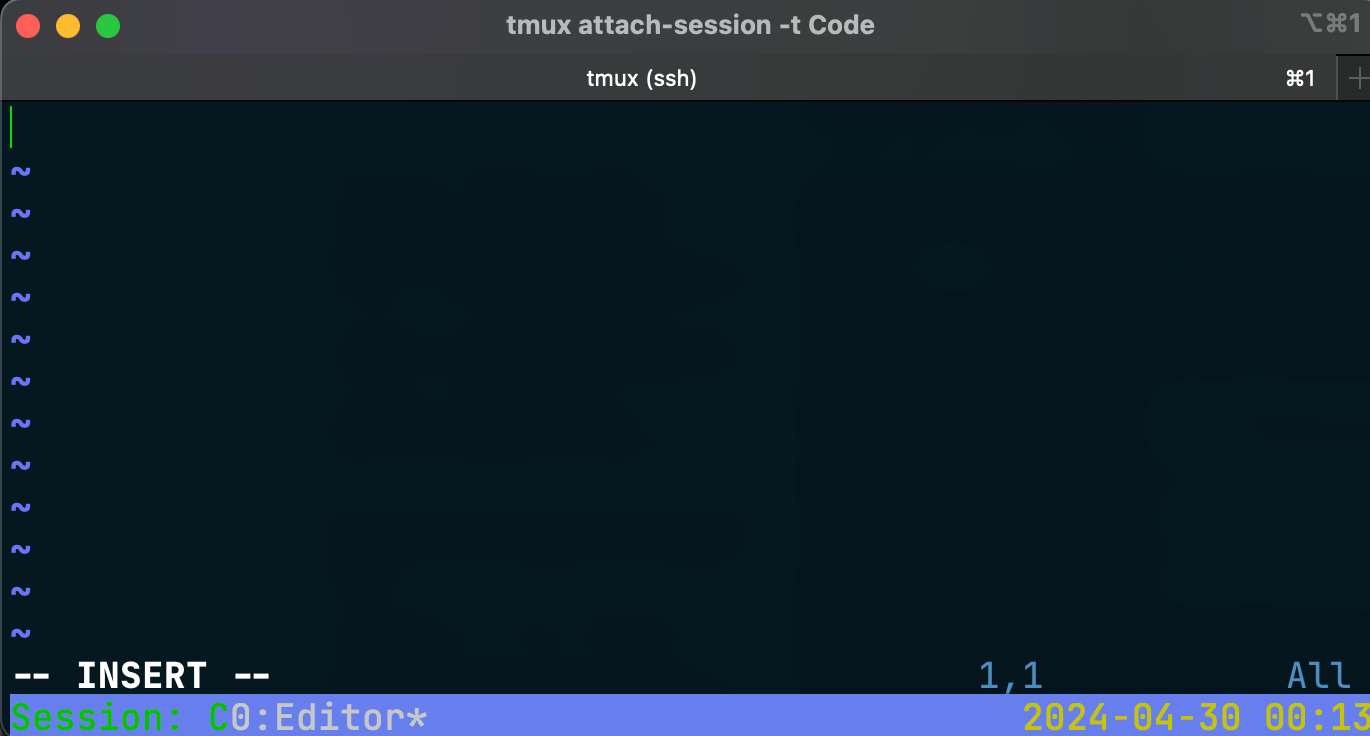
Setup a second pane for running a development server
tmux split-window -h -p 50 -t 'Code' 'nano'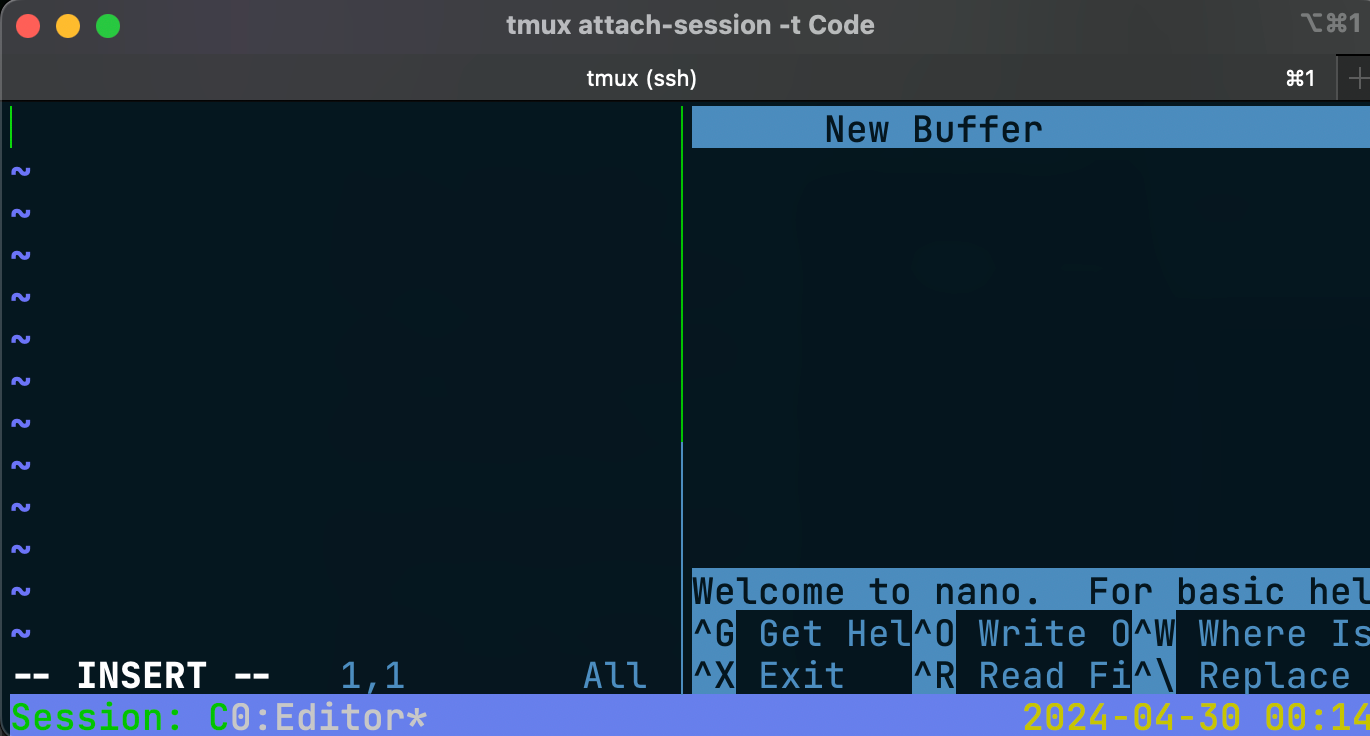
Add a third pane for logs
tmux split-window -v -t 'Code:0.1' 'tail -f startCosmicDefender.sh'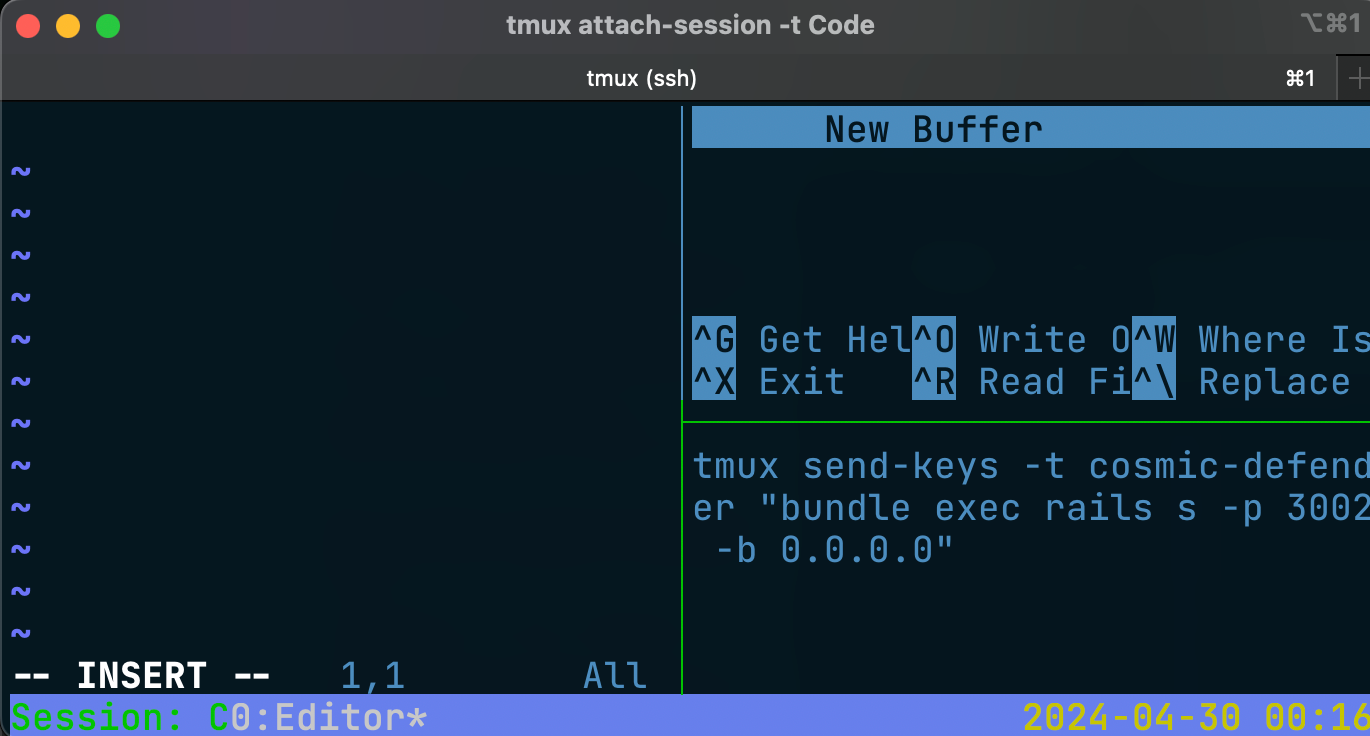
Attach to the new session
tmux attach-session -t 'Code'Why Integrate tmux into Your Workflow?
tmux enhances your terminal handling capabilities, providing robust solutions for managing multiple tasks and maintaining persistent sessions. It's highly customizable, allowing you to tailor it to your specific needs, which can significantly improve your productivity and streamline your development process.
Conclusion
tmux is more than just a tool; it's a system that can revolutionize your approach to managing terminal tasks. With its robust set of features, tmux is essential for anyone looking to boost their terminal productivity.